The Need For Renewable Energy
Energy Glass Solar™, The Best Of Renewable Energy!
Energy Glass Solar™, an alternative energy, patented, optically clear electric producing glass, is not an added cost to a building project as are other alternative renewables. Combined with the Federal Investment Tax Credits (ITC), Energy Glass Solar™ is a less expensive alternative for standard plate glass, saving the builder initial costs and on-going energy costs
Why Renewable Energy?
At least $4 trillion a year needs to be invested in renewable energy until 2030 – including investments in technology and infrastructure – to allow us to reach net-zero emissions by 2050. Four key climate change indicators – greenhouse gas concentrations, sea level rise, ocean heat and ocean acidification – set new records in 2021. This is yet another clear sign that human activities are causing planetary-scale changes on land, in the ocean, and in the atmosphere, with dramatic and long-lasting ramification
The transition to green energy has never been more important. As carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere continue to rise and the earth continues to warm, finding ways to deploy clean, renewable sources of energy like solar, wind, and geothermal power is critical to improving the long-term climate outlook. Derived from natural resources that are abundant and continuously replenished, renewable energy is key to a safer, cleaner, and sustainable world.
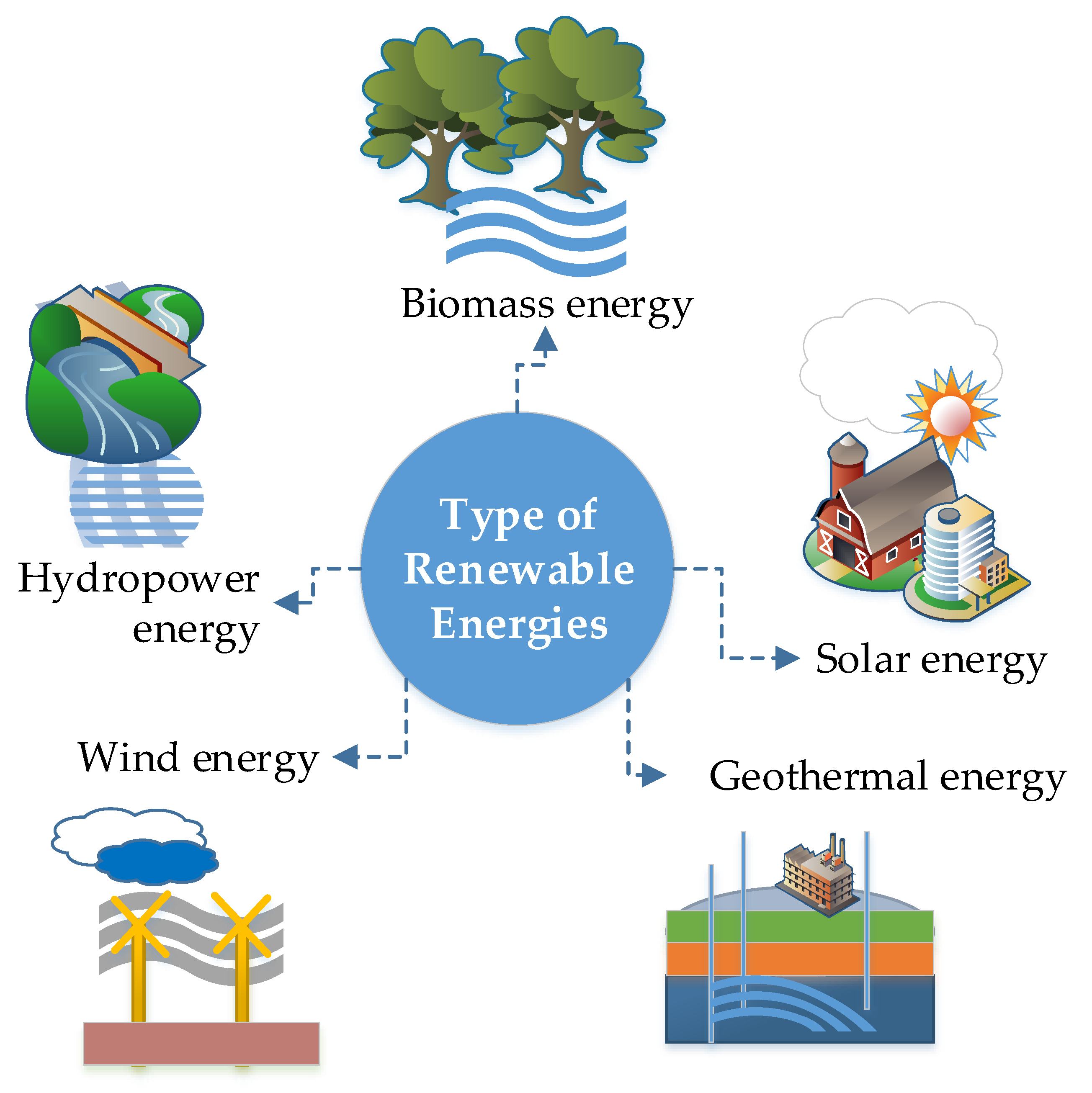
Renewable energy describes a collection of energy technologies, i.e., solar, wind, geothermal derived from sources that are never-ending and can be replenished time after time. Renewable sources are renewable, sustainable, abundant, and environmentally friendly. Unlike fossil fuels, they are not going to expire soon as they are constantly replenished.
The Most Widespread Sources Of Energy
While the advantages and disadvantages of renewable energy exist, the advantages of using renewable forms of energy far outweigh the disadvantages, more so moving to the future.
Wind: This takes advantage of wind motion to generate electricity. Wind motion is brought about by the heat from the sun, and rotation of the earth, mainly via the Coriolis Effect.
Solar: It taps heat from the sun to produce energy for the generation of electricity, heating, lighting homes and commercial buildings.
Hydropower: Utilizes moving water to produce electricity. Moving water creates high energy that can be harnessed and turned into power.
Biomass: Together with snow and rain, sunlight is essential for plant growth. Organic matter that constitutes plants is referred to as biomass, which can be utilized to generate electricity, chemicals or fuels to power vehicles.
Ocean: Takes advantage of rising and falling of tides to generate electricity
Geothermal: Leverages heat from underneath the earth to generate electricity.
Advantages of Renewable Energy
Now Accepting Projects
